Leishmania Life Cycle
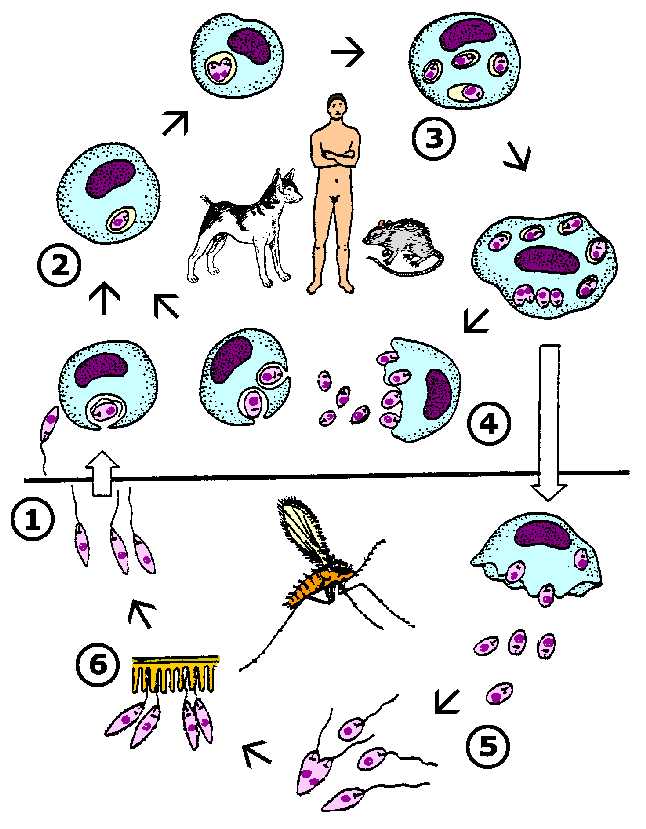
- Metacyclic promastigotes are transferred to the vertebrate host as the sand fly takes a blood meal.
- The promastigotes are phagocytosed by macrophages and transform into amastigotes.
- The amastigotes undergo repeated cycles of binary fission within the macrophage.
- Amastigotes are released from the infected macrophage and re-initiate the replicative cycle in new macrophages.
- If taken up by a sand fly the amastigotes convert to promastigotes and undergo binary fission. These procyclic promastigotes adhere to the gut epithelium to avoid being excreted.
- The procyclic promastigotes quit dividing and undergo a terminal differentiation into metacyclic promastigotes which are infective for the vertebrate host.