3.Biomedical image processing
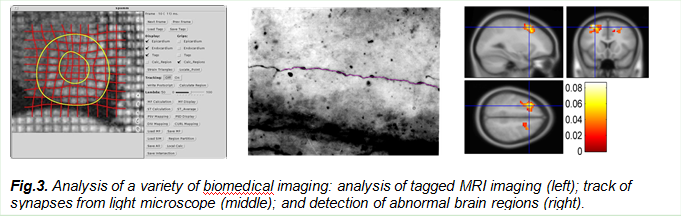
The PI, Dr. Wang, started his career on medical imaging when working as a postdoc at Washington University Medical Center for cardiovascular imaging analysis with tagged MRI. He developed a technique to analyze the movement and deformation of the human heart for clinical diagnosis. Since then, we have made contributions to various biomedical imaging such as optical imaging, microscopic imaging and fMRI imaging, ranging from tissue and organ levels to cellular and molecular levels, as evidenced from my publications.
a. Yu-Ping Wang, Y. Chen, A. A. Amini, Efficient LV Motion Estimation using Subspace Approximation Techniques, IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging, vol. 20, no.6, June 2001
b. Yu-Ping Wang, Y. Wang and P. Spencer, Fuzzy Clustering of Raman Spectral Imaging Data with a Wavelet-Based Noise Reduction Approach, Applied Spectroscopy, 60(7), 60(7), 2006.
c. Yu-Ping Wang, Husain Ragib, and Chi-Ming Huang, A wavelet approach for the identification of axonal synaptic varicosities from microscope images, IEEE Trans. Information Technology in Biomedicine, May, 11(7): 296-304, 2007.
d. Hongbao Cao and Yu-Ping Wang, Segmentation of M-FISH images for improved classification of
We recently received an NSF EPSCoR project with New Mexico, Nebraska, and Louisiana to form a consortium on developmental chronnecto-genomics (Dev-CoG). The overarching goal is to advance understanding of childhood brain connectivity by developing new analytic approaches to study connectivity over brief and extended periods of time (the chronnectome), via multiple neuroimaging modalities. We will continue to develop multivariate approaches for multi-scale longitudinal modeling of developmental changes in multi-modal chronnectomic measures.

